Even the slightest details can make or break a claim in the world of healthcare. One of the most common yet least understood details is the entity code in medical billing. An incorrect or misplaced code can lead to unproductive delays, rejected claims, and unpredicted patient bills. However, precise entity coding supports a smoother medical billing process, quicker payments, and fewer headaches altogether including patients, providers, and payers. All of this is understandable in an operational approach. Everyone expects immediate reimbursement once a patient has a scheduled operation and the provider submits the claim.
However, the claim was refused within a few weeks. What was the reason? Not eligibility. Not a medical necessity. But a mismatched or missing entity code in medical billing. This error leads to unnecessary worry for patients, interrupts cash flow for providers and requires hours of rework for medical billing and coding specialists. This small identifier, frequently overlooked, has a big influence on the medical billing process.
Moreover, this blog will try to explore what is entity code in medical billing, an overview, importance, understanding, types, errors, how to avoid errors, compliance issues and best practices or strategies to use it effectively to reduce denial codes in medical billing, improve accuracy, and keep both patients and providers satisfied in the whole process of entity coding in medical billing.
An overview of Entity Code in Medical Billing
An entity in medical billing refers to the person, organization, or provider who is associated with a claim that is submitted to the insurer to get reimbursement in medical billing. The entity code for medical billing is an exceptional identifier that tells the payer accurately who the billing entity is, whether that is a physician, a lab, a hospital, or the patient. We can think of it similar to a digital signature. Without it, the insurer cannot confirm who performed the service or who should receive the payment.
Why Entity Coding Matter More Than You Think
The healthcare system processes millions of claims every day. Insurers depend on accurate coding to keep things running professionally and accurately. Incorrect entity codes not only slow down the medical billing process but also lead to claim denials, late reimbursements, financial stress for patients, and revenue interruption for all providers.
Mastering entity codes is essential and important for a medical coding specialist. Accurate codes allow insurers to identify the billing entity and approve payments without any delay. The entity code for medical billing is the way insurers can distinguish who is who in all processes.
Just like without a fingerprint you cannot open a lock on your phone or login in to your bank account app, likewise the payer cannot correctly match the service to the right provider without the correct code. This may lead to claim denial even if there is a small or little mismatch or divergence.
However, the following points which make clear why this matters now more than ever:
- Initial claim denials in the U.S. have risen to approximately 15% of all claims and rising denial rates with missing or incorrect data as a main contributor, according to research data from index of Change Healthcare’s 2024 Revenue Cycle Denials.
- Payers depend on automated systems. If the system cannot read the billing entity correctly, it does not just slow down, but it also rejects the claim outright.
- Every rejected claim risks the bill bouncing back to the patient, causing confusion and financial anxiety. Understanding entity codes is no longer optional, but it is essential for professional success, especially for a medical billing and coding specialist.
Pro Tip: Check the entity code against the provider’s NPI and tax ID before filing any claims. Only a single digit error can end up in a denial, delay reimbursement, or divert payment, costing the patient and practitioner money and time.
Understanding Entities in the Medical Billing Process
What does “entity” essentially represent following that?
In simple terms to understand:
- The billing entity is the party demanding payment.
- The rendering entity is the provider who accomplished the service.
- The referring entity might be the physician who sent the patient for supplementary care, such as a lab test, etc.
Each plays a role in how insurers process claims and without manifestly identifying these entities, claims can straightforwardly be denied.
Types of Entity Codes in the Medical Billing
Entity codes are identifiers or identifications used to identify or explain the role of individuals, practices, or payers in the medical billing process. Moreover, these codes bring clarity in claims, connecting patients, providers, and insurers accurately. They can be grouped into various categories or types:
Pro Tip: Keep an easy access of “Entity Code Guide” at your workstation or within your billing software. Knowing the difference between a billing, rendering, and referring entity code can save hours of troubleshooting and helps you to ensure every claim is matched to the right provider the first time.
1. Entity Roles in Billing Transactions
These codes are used to recognize the role of the individual or practices in a claim:
- Subscriber – Someone who is the policyholder protected under the health insurance plan.
- Dependent – A person covered under the plan of the subscriber such as a child or spouse.
- Provider – Anyone who can be a doctor, nurse, physician or healthcare professional delivering or rendering care.
- Payor – This is the insurance company from which the subscriber has purchased coverage.
2. Functional Entity Codes in Claims
These are frequently used to identify or specify the particular responsibility in a claim:
- Billing Entity Code – This identifies the person or group submitting the claim.
- Rendering Entity Code – This code identifies the provider who performed or rendered the service.
- Referring Entity Code – This code identifies the provider who referred the patient for extra care.
- Supervising Entity Code – This is used when another provider supervises a service.
- Secondary Entity Codes – This is used for additional services like labs, radiology or anesthesia.
3. Entity Identification Numbers or Entity ID Codes
These Entity ID codes or numbers are common and standardized identifiers used for providers, payers, and practices. These entity codes or numbers are:
- National Provider Identifier (NPI) – This is a 10-digit entity ID for medical practices and practitioners in the United States.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN) – These businesses are divided into groups or categories applying this for purposes of taxation.
- Health Plan Identifier (HPID) – In everyday electronic transactions, this distinguishes health plans.
- Tax Identification Number (TIN) – This is used by facilities and businesses for tax transactions.
- Unique Physician Identification Number (UPIN) – This entity is used to identify individual physicians, the UPIN has been mostly replaced by the NPI but it may still be relevant in certain circumstances.
4. Entity Types by Healthcare Practice
These entity codes also indicate the type of provider or facility:
- Physicians (Doctors) – These are individual providers involving generalists and specialists.
- Nurse Practitioners (NPs) – They are advanced practice providers delivering primary care.
- General Hospitals – These are acute care hospitals dealing with a wide range of medical requirements.
- Specific Hospitals – These are specialty hospitals treating particular conditions such as cancer centers.
- Independent Clinics – These are clinics offering specialized or outpatient services.
- Nursing Homes – These facilities are providing long-term care for elderly patients.
- Clinical Laboratories – These are labs offering diagnostic and testing services.
5. Entity Types by Health Plan or Insurance
Lastly, these entity codes also implement to the payer side:
- Commercial Health Plans – This is a private insurance coverage purchased by individuals or employers.
- Medicaid – It is a governmental medical insurance plan for lower-income individuals as well as their families.
- Medicare – Medicare is a federal health insurance program for aged people and over 65.
Entity Related Common Errors in Coding and Claims
Entity codes are a common source of mistakes despite their importance. Additionally, spotting these errors before submission can avoid costly delays for a medical billing and coding specialist. These common errors include:
- Entering the incorrect or wrong billing entity such as group vs. individual.
- Using out-of-date provider information.
- Leaving the field blank in the information document.
- Mistakes in the Typos such as typing or printing during the entity code for the medical billing process.
- Unclear and confusing rendering and billing providers.
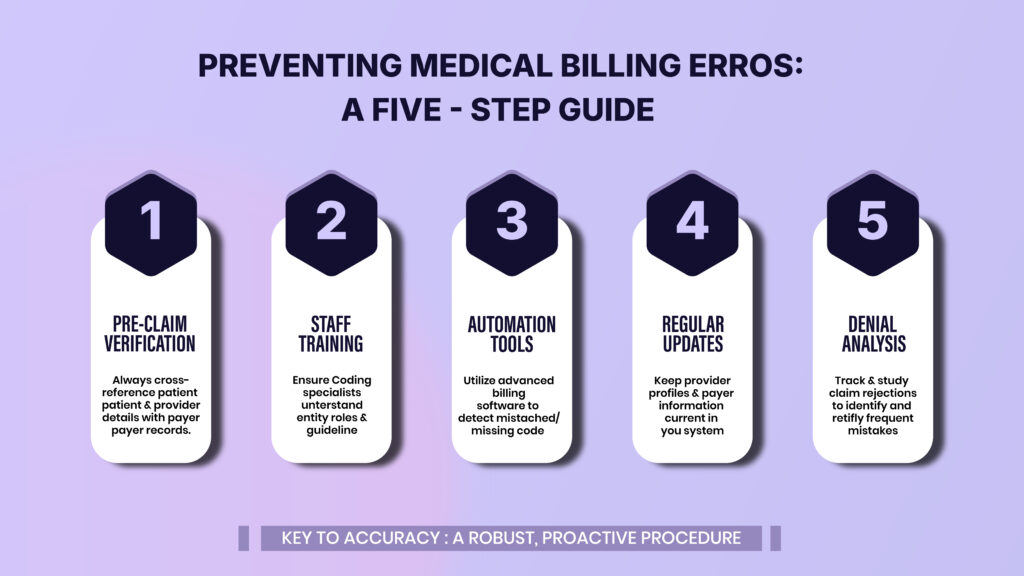
How to Avoid Errors in Coding and Claims
The best way to circumvent entity errors is by building a procedure that prioritizes accuracy. Resolutions for these errors include:
- Pre-claim verification – Always check that entity details or specifics match payer records.
- Staff training – This is important to confirm that every medical coding specialist understands the role of entities.
- Automation tools – Uninterruptedly use modern and emerging technological billing software to catch mismatched or missing codes.
- Regular updates – Continuously retain provider profiles up-to-date in your billing system.
- Denial analysis – Continually follow track and study rejections to identify frequent mistakes.
What are the Entity Code Denial and Rejection Reasons?
An entity code denial happens when a payer rejects or denies a claim due to incorrect or missing entity information. However, these rejections usually come with specific denial codes in medical billing such as:
- Entity not recognized or documented
- Billing provider not eligible or inappropriate
- Rendering provider mismatch for services
Rejections can occur for many reasons, including:
- Wrong or missing billing entity particulars and details.
- Provider or practices not registered with the payer.
- When using an old or inactive NPI.
- Confusing and unclear group vs. individual codes.
- Payer-specific formatting requirements not being followed or adopted.
How Entity Codes Influence Medical Billing
Entity codes play an essential role in the whole medical billing and coding system. They act as the backbone of claim processing from identifying providers to routing payments. For providers, accurate codes mean timely revenue. For patients, it means there are fewer clashes. It means cleaner information or data for payers. Moreover, it is proof of professional accuracy for a medical billing and coding specialist.
Advance Strategies for Best Practices
Consequently, how do you circumvent the trap? The answer always lies in accuracy and validation. There is a rule of healthcare billing that thinks of it as the “measure twice and cut once.” However, practices that implement these steps frequently report 20 to 40% fewer denials and a visible improvement in patient satisfaction because bills get fixed faster.
Here are the following proven strategies and approaches for best practices:
- Train your team to enter provider details consistently. Even small differences such as “St.” vs. “Street” can cause mismatches. You need to standardize data entry.
- Cross-check entity codes with payer databases before submitting claims. Many insurers deliver online tools for validation, such as software.
- Use billing software to auto-populate entity codes in medical billing based on kept profiles because automation reduces human error and validates entity data.
- Run an internal assessment before submission because a quick check avoids long weeks of reprocessing.
- A certified medical coding specialist knows how to navigate payer-specific quirks, ensuring the billing entity is recognized correctly.
- Keep updated records of every provider, facility, and lab your practice works with. You can create a “master list” of entities and maintain a centralized entity database.
- Make sure their insurance card and demographics are accurate before services are billed, and you can educate patients upfront for accuracy.
- If you spot repeated denial codes in medical billing tied to entities, you know where the gap is and always use a denial tracking process.
Pro Tip: Create a simple “Claim Accuracy Checklist” that includes entity code verification before submission. This quick extra step of just 60 seconds per claim, can prevent weeks of delays, reprocessing headaches, and lost revenue, keeping your cash flow and patient trust strong.
Benefits of Correct Entity Code Usage
Why is entering the correct entity code so noteworthy? Because it:
- Decreases denials and rejections.
- Enhance and speed up reimbursement.
- Advances the accuracy of the medical billing process.
- Lesson’s patient stress from surprise bills.
- Increased provider belief in billing teams.
Hidden Pitfalls Need to Watch Out
Whereas best practices assist you but mistakes still lurk where you least expect them. However, watch out for these:
- Over-reliance on software – Automation supports but it is only as good as the data you provide it.
- Confusing rendering vs. billing providers – The doctor who made the service is not always the one submitting the claim. Together may need entity codes.
- Skipping updates during staff turnover – When providers leave or join, their entity essentials must be up-to-date instantly.
- Ignoring payer-specific rules – One insurer may involve the group’s entity code; another may request the individual providers.
- Forgetting secondary claims – When billing for labs, radiology, or anesthesiology each service line might need a diverse billing entity. Avoiding these downsides keeps your claims channel healthy and efficient.
HIPAA Compliance and Entity Codes
Entity codes are connected to the compliance with HIPAA alongside billing. As a way to make certain that patient data has a close connection with the appropriate entities, HIPAA requires authentic provider identification. Problems with compliance may arise from incorrect entity coding, particularly when claims have been sent to the incorrect entity or provider. The confidentiality of information and privacy can be maintained by using the correct codes.
How iSolve RCM supports You in Entity Code for Medical Billing
We are aware that every little mistake, such as providing the wrong or incorrect entity code, can end up in costly delays or the rejections of claims. Therefore, our team of experienced medical billing services and coding specialists takes a practical approach to bring accuracy at every step of the medical billing process. We rationally validate billing entities, double check entity ID numbers such as TIN, NPI and EIN, and monitor compliance with payer requirements to decrease the risk of rejections or denials. We train providers and staff about common drawbacks, from entity code denials to HIPAA-compliant problems and give them confidence in their revenue cycle. Healthcare practices gain a righthand partner who not only handles the complication of entity coding in medical billing but also turns it into a strength for quicker reimbursements, less denials, and a smoother claims journey with iSolve RCM.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of an entity code?
An example is the Billing Entity Code, which recognizes the provider or practice submitting a claim. Other examples include referring, rendering, and supervising Entity Codes.
How to fix entity code in medical billing?
Review or evaluate the denial or rejection notice, validate the correct entity ID number, and update the claim before resubmitting.
What does it mean when a claim is rejected for an entity code?
It means the payer could not match the submitted entity code or ID number with its records, frequently due to errors, discrepancies and mismatches, or misplaced data.
How do I find my entity code?
You can detect your entity code on your NPI registry, IRS documentation, or payer enrollment records, conditional on the type of entity.




