The medical claims are a story and all details matter. Every line item represents a service offered, department and cost, which should be well explained to insurance payers. However, a lot of claims are denied or rejected due to minor mistakes or misinterpretations. Lack of clarity around revenue codes is one of the most widespread areas of problems. Medical billing requires to know what is a revenue code in medical billing to properly submit claims and receive reimbursement in time.
Revenue codes classify hospital services into the standard billing terminologies that can be accepted by payers. They associate particular services including routine diagnostics and complicated surgical interventions to the departments where the care was provided. Such a system provides uniformity, clarity and precision in billing of facilities.
This blog describes the concept of revenue code in medical billing, its use in hospital and Medicare claims, and the fact that payers pay close attention to it. It also points out inpatient and surgery revenue codes and its practical effect on denials reduction and better reimbursements accuracy through outsourced medical billing services.
What is a Revenue Code in Medical Billing?
In medical billing, a revenue code is a four-digit numeric code assigned to hospitals and healthcare facilities that is mostly applied to identify the department or type of service offered when a patient visits the facilities. Such codes do not outline the specific procedure done, and instead, it classifies services including room charges, lab services, radiology, pharmacy or use of the operating room. It is critical to know the meaning of a revenue code in medical billing since it allows insurance payers to identify the areas where a service was provided in the facility.
The types of revenue codes are reported on the institutional claims, e.g. the UB-04 form, and are particularly vital in the inpatient and outpatient hospital billing. They are used to complement the use of procedure codes such as CPT or HCPCS to ensure proper reimbursement and procedure claims. To put it simply, revenue codes make sure that healthcare revenue cycle management services are appropriately bundled, billed and paid as per the requirements of the payers.
Pro Tip: It is always important to cross-check the revenue code with the hospital chargemaster and the corresponding CPT/HCPCS code to ensure that the billing process is accurate and does not result in denied claims. Using the correct code makes the process of reimbursement much easier.
Importance of Revenue Codes in Medical Billing
The significance of revenue codes in billing of medical services is the role of revenue codes, which ties medical services to the relevant hospital departments and cost centers. Such codes assist insurance payers in a fast manner as to comprehend where a service was given, and the kind of facility resource was consumed. A properly used revenue code in medical billing will facilitate the proper reporting of charges, minimize confusion in the process of claims being reviewed, and facilitate the standardization of the way services are grouped.
Revenue codes also have a significant contribution in timely reimbursement and approval of claims. Wrong or absent revenue codes may result in denials, delays or underpayment, particularly institutional and inpatient claims. Healthcare organizations can enhance compliance, increase billing accuracy and have a smoother revenue cycle in general with the assistance of the right revenue codes and medical coding.
Implication of Revenue Codes in Health Care Finance
Revenue codes maintained by the National Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC) in the U.S which standardizes them for institutional claims and are essential in the management and monitoring of healthcare services in terms of finances. In health care finance, a revenue code in medical billing assists in categorizing services by department e.g. in the laboratory, radiology, pharmacy or inpatient care.
This categorization enables hospitals and other health institutions to track the usage of the services, cost allocation and departmental performance. In the absence of revenue codes, there would be disparities in correlating clinical services to financial information.
In addition to in-house tracking, revenue codes medical billing aids in reimbursement and financial reporting. Such codes are essential since they enable payers to authenticate charges, implement payment regulations, and estimate reimbursements, particularly where the facility claims are concerned. Proper utilization of revenue codes enhances financial transparency, aids financial budgeting and forecasting, and assists healthcare organizations to have a steady cash flow without violating payer and regulatory rules.
Structure of a Revenue Code
The revenue code in medical billing is a four-digit number that identifies hospital services for billing purposes. Each digit has a special meaning. The first digit identifies a broad category of service, like room and board, pharmacy, radiology, or surgery. First three digits identify a broad type of service within a category like 010-099 for room and board, 450-459 for emergency room. Fourth digit identifies a specific type of service, like type of room, minor vs. major surgery, or the specific surgical suite used.
Revenue Code Applications in Various Medical Facilities
Revenue codes can be used to classify services according to the nature of care and the department where the services are delivered. Various healthcare facilities, such as hospitals, clinics, and outpatient facilities, have their own set of revenue codes.
1. Revenue Codes for Inpatient Services
Inpatient services use revenue codes to capture the cost of hospital stays, including room and intensive care.
Following are common Inpatient Revenue Codes:
- 0100–0219 cover room and board charges, including different bed types such as general medical and semiprivate.
- 0200–0209 represent Intensive Care Unit (ICU) services, including general and specialized types like surgical or pediatric ICU.
- 0210–0219 cover coronary care unit types.
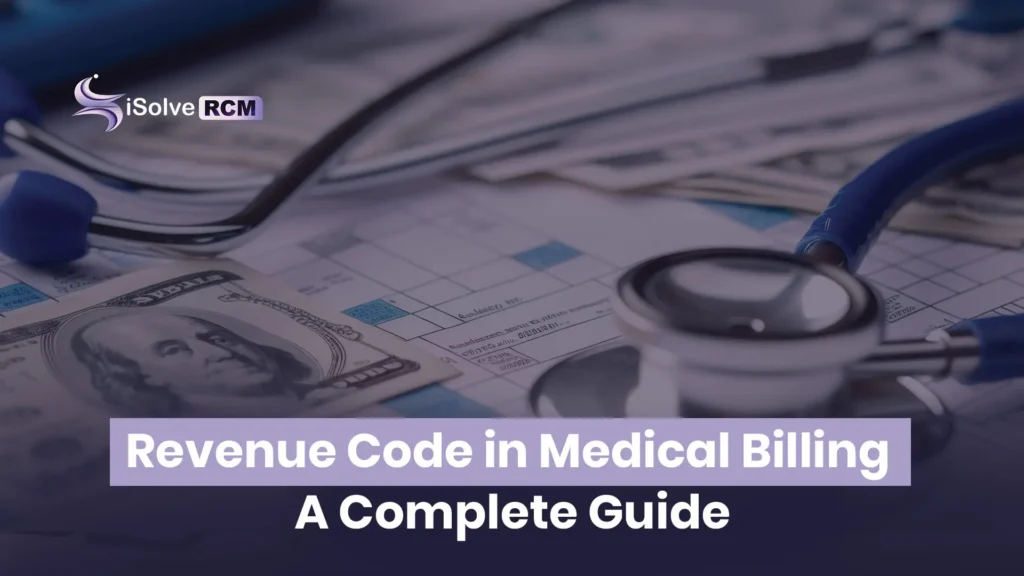
2. Revenue Codes for Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
ICU revenue codes apply to patients who require continuous monitoring and high‑level care.
Following is the ICU Revenue Code List:
- 0200 covers general ICU services for critically ill patients.
- 0201 represents care provided in the Surgical ICU.
- 0202 includes services in the Medical ICU.
- 0203 covers Pediatric ICU services for children.
- 0204 represents care in the Psychiatric ICU.
- 0206 includes post-ICU care services.
- 0207 covers specialized Burn Care ICU services.
- 0208 represents Trauma ICU services.
- 0209 includes other ICU services not classified under specific types.
3. Revenue Codes for Pharmacy
Pharmacy revenue codes identify medications and services related to drugs provided by a facility.
Following are Pharmacy Revenue Codes:
- 0250 covers general pharmacy services within the facility.
- 0251 represents dispensing of generic drugs.
- 0252 includes non-generic (brand-name) drugs.
- 0254 covers pharmacy drugs provided incident to other diagnostic services.
- 0255 represents drugs administered incidental to radiology procedures.
- 0257 includes non-prescription (over-the-counter) drugs.
- 0258 covers intravenous (IV) solutions provided to patients.
- 0259 represents other pharmacy services not classified above.
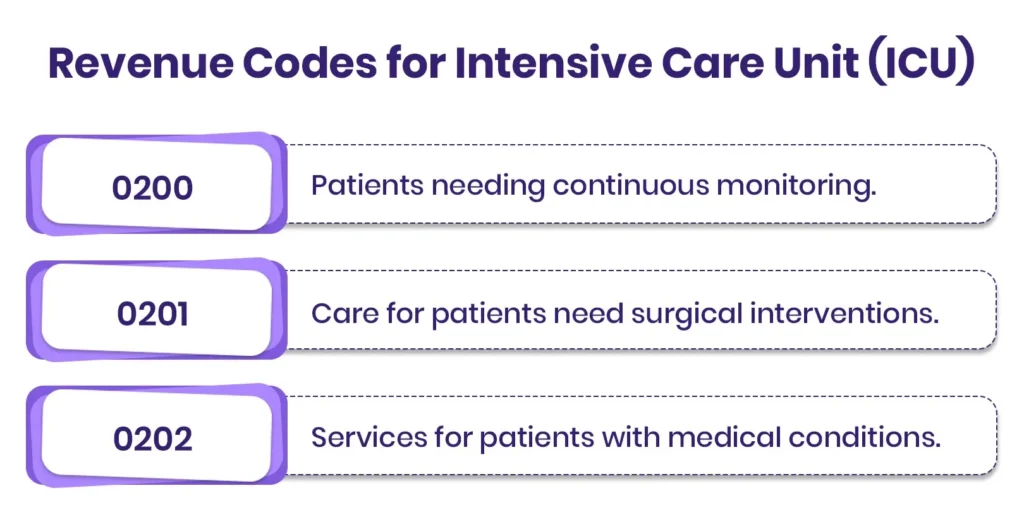
4. Revenue Code for Laboratory
Lab revenue codes represent clinical diagnostic tests and specimen processing services and need to be billed based on complete laboratory billing guidelines in order to correctly classify, follow compliance, and attain proper reimbursement.
Following are Laboratory Revenue Codes:
- 0300 covers general laboratory services provided to patients.
- 0301 represents chemistry lab tests, such as blood chemistry panels.
- 0302 includes immunology laboratory tests.
- 0304 covers non-routine dialysis laboratory services.
- 0305 represents hematology lab tests, including blood counts and related studies.
- 0306 includes bacteriology and microbiology lab services.
- 0307 covers urology-related laboratory services.
- 0309 represents other laboratory services not classified under specific categories.
5. Revenue Codes for Radiology
The Radiology revenue codes are utilized to classify the diagnostic imaging and certain therapeutic imaging services, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and other radiology billing and coding for correct reimbursement.
Following are Radiology Revenue Codes:
- 0320 covers general diagnostic radiology services.
- 0321 represents angiocardiography procedures.
- 0322 includes arthrography imaging studies.
- 0323 covers arteriography procedures.
- 0324 represents chest X-ray imaging services.
- 0329 includes other radiology services not classified under specific categories.
6. Revenue Codes for Operating Room
Operating room revenue codes are used to report charges for use of surgical facilities.
Following are Operating Room Revenue Codes:
- 0360 covers general operating room (OR) services provided during surgical procedures.
- 0361 represents minor surgical procedures performed in the OR.
- 0362 includes organ transplant surgeries, excluding kidney transplants.
- 0367 covers kidney transplant procedures specifically.
- 0369 represents other operating room services not classified under specific categories.
7. Revenue Codes for Physical Therapy
Physical therapy revenue codes cover rehabilitative and therapeutic services. In the billing of physical therapy services, such as Neuromuscular Reeducation CPT Code 97112, the use of the correct revenue code is important for correct classification and timely payment.
Following is the Physical Therapy Revenue Codes:
- 0420 covers general physical therapy services provided to patients.
- 0421 represents charges for individual physical therapy visits.
- 0422 includes hourly charges for physical therapy sessions.
- 0423 covers group physical therapy rates.
- 0424 represents evaluation or re-evaluation services in physical therapy.
- 0429 includes other physical therapy services not classified above.
8. Revenue Codes for Clinics
Clinics, whether outpatient specialty or general facilities, also use revenue codes to categorize services for accurate billing and reimbursement. Revenue codes in a clinic environment assist in determining the nature of the service delivered, the location, and the level of care, which is vital for insurance reimbursement and accurate facility reporting.
In the billing services associated with particular medical conditions, such as Abnormal Weight Gain ICD-10 Code R63.5, the use of the correct revenue code is important for alignment with payer requirements.
Following are common Clinic Revenue Codes:
- 0510 covers general clinic services, typically used for routine outpatient visits.
- 0511 represents services provided in rural health clinics.
- 0512 includes physician clinic services for general medical care.
- 0513 covers specialty clinic services, such as cardiology or dermatology.
- 0514 represents obstetrics and gynecology clinic services.
- 0515 includes pediatric clinic services for children.
- 0516 covers psychiatric or behavioral health clinic services.
- 0519 represents other clinic services not classified under specific categories.

9. Revenue Codes for Emergency Room Visit
Emergency room (ER) revenue codes capture services provided during emergency visits.
Following are common Emergency Room Codes:
- 0450 covers general Emergency Room services for patients.
- 0451 is used for EMTALA Emergency Medical Screening Services.
- 0452 represents ER services provided beyond EMTALA screening.
- 0456 includes care provided in Urgent Care settings.
- 0459 covers other miscellaneous Emergency Room services not classified elsewhere.
10. Revenue Codes for Outpatient Services
Outpatient services include visits where patients are not admitted but receive treatment or diagnostics.
Following are common Outpatient Revenue Codes:
- 0500 covers general outpatient services provided in the facility.
- 0509 represents other outpatient services not classified under specific categories.
- 0510–0519 includes clinic services such as dental, psychiatric, OB/GYN, pediatric, and other specialty clinics.
Pro Tip: It is always important to check the revenue code against the location of service and type of care delivered. This is to ensure accuracy. Cross-checking with the hospital chargemaster and the guidelines of each insurance company will help prevent denied claims. Using the correct revenue code will not only simplify the billing process but also ensure that each department receives the correct reimbursement for services delivered.
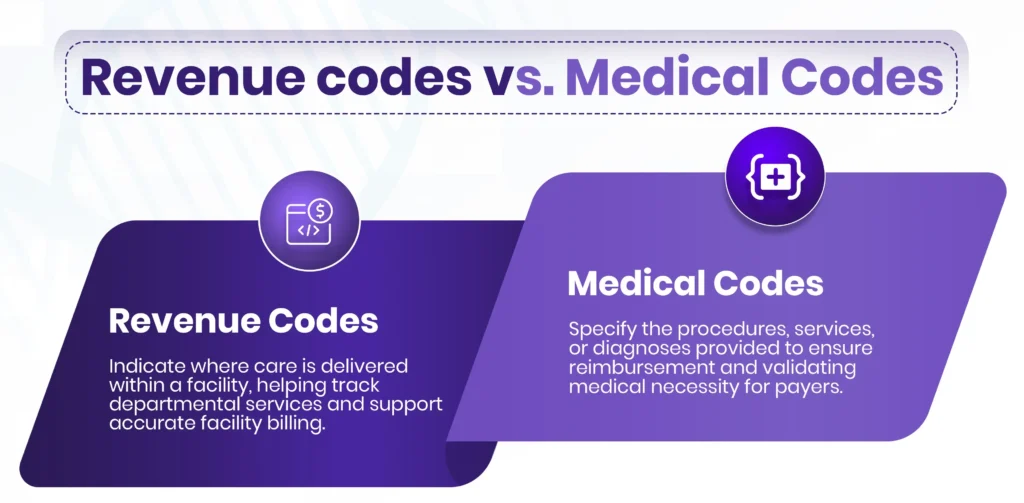
Revenue Codes Vs Medical Codes: What is the difference?
Revenue codes show the location of the services provided within the facility and are necessary for hospital billing as well as tracking the cost of rendered services. Medical codes describe the services provided be it a procedure, service, or diagnosis. Both work as a team to aid in the reimbursement of services provided.
| Aspect | Revenue Codes | Medical Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify department or service location. | Describe the procedure, service, or diagnosis. |
| Focus | Where care is delivered. | What care is delivered. |
| Examples | 0120 covers the general medical/surgical floor. | 99213 cover office or outpatient visits. |
| Used By | Hospitals, facility-based billing. | Physicians, clinics, and hospitals. |
| Forms | UB-04 for institutional claims. | CMS-1500, electronic claims. |
| Level of Detail | Broad classification such as department or service type. | Specific service, procedure, or diagnosis. |
| Function in Billing | Supports facility cost tracking and reimbursement | Supports payer approval based on medical necessity |
| Standardization | Maintained by CMS and hospital guidelines | Maintained by AMA (CPT), WHO (ICD-10), CMS (HCPCS). |
| Time Sensitivity | Usually per patient stay, visit, or department use. | Usually per procedure, encounter, or treatment session |
| Impact on Payment | Determines facility reimbursement rates. | Determines service coverage and payment accuracy. |
| Audit or Reconciliation Use | Used in revenue cycle management and departmental accounting | Used in compliance audits, clinical review, and claim validation. |
| Coding Complexity | Relatively simple numeric system | More complex; includes alphanumeric codes with modifiers and detailed descriptions |
| Examples by Category | 0360 cover operating room and 0300 cover Lab services | 81002 – Urinalysis, 70450 – CT scan without contrast. |
| Interdependency | Works with medical codes to validate claims | Requires revenue codes to ensure the correct facility charge classification |
Revenue Codes Vs. CPT Codes/HCPCS Codes
Key Differences Between Revenue Codes and CPT Codes
Revenue codes are four-digit numeric codes used in facility billing to identify the department, type of service, or location where care was delivered such as ICU, radiology, or pharmacy. They answer questions such as “Where was the service provided?”
CPT codes also known as Current Procedural Terminology codes are five-digit alphanumeric codes used to describe specific medical procedures or services provided by healthcare professionals. They answer questions such as “What service was performed?”
Following are the key differences:
- Revenue codes categorize facility resources, while CPT codes describe clinical procedures.
- Revenue codes are required for institutional claims such as form UB-04, whereas CPT codes are primarily used for professional claims such as CMS-1500.
- Revenue codes focus on billing accuracy for the facility; on the other hand, CPT codes focus on medical necessity and service documentation.
Revenue Codes vs. HCPCS Codes
HCPCS also known as Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System extend CPT codes to include items not covered in CPT, such as:
- Durable medical equipment (DME)
- Ambulance services
- Certain drugs and supplies
In institutional claims, revenue codes still define where services occurred, while HCPCS codes define specific items or non-physician services provided. For example:
- Revenue code 0250 is used for Pharmacy.
- HCPCS J0696 is used for injection of medication.
Why Both Are Required on Facility Claims
Facility claims like hospital or outpatient clinic UB-04 claims require both revenue codes and CPT/HCPCS codes because:
- Revenue codes indicate which department or cost center provided the service.
- CPT/HCPCS codes indicate the specific procedure or treatment delivered.
Together, they ensure the claim is fully understood by payers which allow accurate reimbursement. Without either code, the claim could be denied or misclassified. For example, a charge for a CT scan in the radiology department would require:
- Revenue code 0320 which is used for radiology services.
- CPT 70450 which is used for CT scan without contrast.
Professional (CPT/HCPCS) Vs. Institutional (Revenue Codes)
Professional billing is based on the professional activities done or the service rendered to the patient by the provider. This is based on the determination of payment through the use of the CPT codes or HCPCS codes. Institutional billing is based on the use of the resources utilized by the facility, where the classification is made through the use of the revenue codes or the use of the hospital departments.
| Aspect | Professional Billing (CPT/HCPCS) | Institutional Billing (Revenue Codes) |
|---|---|---|
| Form Used | CMS-1500 | UB-04 |
| Coding Focus | Procedure/service provided by provider | Department/location where service was delivered |
| Examples of Codes | 99213 – Office visit, 81002 – Urinalysis | 0300 – Lab, 0360 – Operating room |
| Primary Users | Physicians, clinicians | Hospitals, outpatient facilities |
| Payment Determination | Based on procedure and provider work | Based on facility resources and department costs |
| Payer Requirement | Used to validate medical necessity | Used to classify facility charges |
The Question of Finding the Right Revenue Code
It is necessary to find the right revenue code to bill and receive prompt reimbursement. Healthcare professionals and coders can rely on a number of credible sources and methods:
Hospital Chargemaster
The hospital chargemaster is an all-inclusive internal database that contains every billable service, supply, and procedure and the code of revenue related to them. The initial point of reference is usually where coders get to know which revenue code to use when dealing with medical billing of any service or department. The approach of using the chargemaster creates uniformity of the claims of all the facilities.
Medicare Revenue Code List
Medicare maintains an official list of revenue codes organizing the services according to their types and departments. This resource may be used especially in the medical coding of Medicare revenue codes, since the federal billing requirements can be adhered to and assist in avoiding claim denials. This list is used frequently by coders when they are filing claims on behalf of Medicare beneficiaries.
Guidelines to Payer-specific Billing
Insurance payers can possess their own revenue code usage rules, such as department codes or types of services. Considering the payer-specific guidelines of billing would ensure that the selected revenue code is related to the expectations of the payer, which would enhance the accuracy of claims and minimize the probability of claims being denied.
Billing Software and Coding Tools
Current billing software can frequently have inbuilt coding tools and searching features, which are useful in assisting coders to select the right revenue code as fast as possible. The tools are able to cross-reference CPT/HCPCS codes, departmental data, and payer rules to make it easier to make sure that the claim is accurate and meets the industry standards by a medical billing company in USA. A combination of these sources is an assurance of proper revenue coding and an easy revenue cycle management.
Pro Tip: It is always important to cross-check the revenue code selected with the hospital chargemaster, Medicare list, and payer guidelines to ensure accuracy. The use of billing software with coding capabilities can help expedite the process and minimize the chances of claim denial.
Common Revenue Code Errors That Cause Claim Denials
Errors in revenue codes are among the most common causes of denied or delayed claims for hospital and facility claims. An error in revenue code, no matter how small, such as an incorrect department code or a missing digit, can result in the rejection of a claim by the insurance company. Correct revenue coding in medical billing is essential to ensure that services are correctly classified.
Following are the common Revenue Code Errors:
- Applicability of incorrect revenue code to the service given such as lab code instead of radiology.
- Failing to give a revenue code on a claim.
- Choosing a code that is not in line with the setting of the patient like inpatient or outpatient.
- The use of outdated code or invalid revenue codes.
- Assigning the incorrect revenue codes and CPT/HCPCS procedure codes.
- Wrong application of 4-digit modifiers which describe service information.
- Multiple revenue codes of the same line of services.
- Application of generic codes in a case where a more specific code is required.
These mistakes can be avoided to enhance claim acceptance, and reimbursement will be faster, and payer and regulatory policies will be adhered to.
Best Practices in the Assignment of Accurate Revenue Code
Proper revenue code assignment and facilitation of medical billing and reimbursement is necessary. Appropriate medical billing is possible through proper use of revenue code, as services will receive appropriate distribution, the claims will be promptly processed and the denial based on the coding mistake will be minimized. Following best practices will assist health facilities to be compliant, simplify the revenue cycle, and enhance financial performance:
Verify Service & Patient Setting
Prior to a revenue code being assigned, make sure that you have the type of service being given and the setting of the patient, inpatient, outpatient or in the case of an emergency. This is in order to make sure that the code is appropriate to the department and level of care. Denials are often due to misalignment between service and setting.
Reference to Hospital Chargemaster
The chargemaster in the hospital gives a detailed list of all the services that can be billed and the revenue codes associated. Always reconcile services to the chargemaster to be consistent and correct throughout all the claims.
See lists of Official Revenue Code
Consult such resources as the Medicare revenue code list or payer-specific codes to make sure that the chosen code is up-to-date and pertinent. This is because updating code lists will help to avoid mistakes that occur due to the aging or obsolescence of codes.
Match Revenue Codes and CPT/HCPCS Codes
The codes on the claim which relate to the process or service should be the revenue codes. As an illustration, a CT scan is expected to be coded as much as the radiology revenue code and the appropriate CPT code. The alignment minimizes denial of claims in cases of coding errors.
Take Advantage of Billing Software and Coding Tools
The current billing software is usually designed with automated suggestions, cross-references and validation tools that can assist the coder in picking the right revenue code within a very short period of time. The use of these tools will minimize the number of errors that are made manually and enhance the accuracy of claims.
Regular Training and Audits
Continuous training of coders and internal audits are also recommended to make sure that the staff know the existing revenue codes, payer requirements and traps. Regular inspection of allocated codes may detect mistakes prior to submission of claims thereby enhancing efficiency in the revenue cycle.
How iSolve RCM Help with Revenue Code in Medical Billing
Revenue code assignment is a process that requires the combination of knowledge, resources and technology and the adherence to these best practices will guarantee submission of claims in the right format and receive payment in a timely manner. Proper selection of revenue codes is essential to effective medical billing and prompt reimbursement, yet it may be quite tricky to manage it when using multiple services, departments, and payers since iSolve RCM offers an integrated platform that automates the process of revenue code selection, cross-refers CPT/HCPS codes, and maintains adherence to payer-specific guidelines.
iSolve RCM allows healthcare facilities to minimize mistakes, avoid claim reimbursement, and simplify the revenue cycle, making the revenue coding process more precise, efficient, and reliable with the help of such features as real-time validation, billing dashboards, and reporting tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What is a revenue code in billing?
In medical billing, a revenue code is a four-digit numerical code that is used to categorize services in a facility or department within a hospital, used to identify the type of care or department of a hospital or healthcare facility. It determines the location that a service was given like radiology, pharmacy or surgery and assists in the correct claims and performance.
What is the distinction between a procedure code and a revenue code?
A procedure code such as CPT or HCPCS is used to define the medical service or treatment that has been done. Revenue code refers to the department or kind of service in the facility. The code of revenue is used to classify the location that the service is offered, and the procedure code identifies the clinical service to be properly billed.
Is it possible to charge revenue code without a CPT code?
Revenue codes may be included on facility claims without a CPT code, particularly where the services involved are inpatient or departmental. Nevertheless, to indicate professional or procedural billing, the revenue codes are most often accompanied by CPT/HCPCS codes to record the service rendered and make sure it is reimbursed correctly.
What are the sources of revenue codes?
Standard institutional billing systems are the basis of revenue codes. Hospitals provide services with codes depending on its nature of care and department. They are also enumerated in the sources such as the hospital chargemaster and the official Medicare revenue code lists to ensure the right billing practices.
Who maintains revenue codes?
In the U.S., revenue codes are referred to as institutional claims with the National Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC) maintaining the revenue codes. Compliance, accuracy, and consistency in medical billing among medical facilities are ensured by the provision of official revenue code lists and updates by Medicare and other payers.
What are the three main types of medical codes?
The three main types of medical codes are:
- Diagnosis codes (ICD-10) which identify patient conditions or diseases.
- Procedure codes (CPT/HCPCS) which describe medical services or treatments.
- Revenue codes which categorize the location or type of service provided within a facility for billing purposes.